Rate Equation
Rate Equation: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Order of a Reaction, Mechanism of a Reaction, Molecularity of a Reaction, Preparation of Sulphuric Acid by Contact Process, Elementary Reactions, Rate Determining Step, Unimolecular Reaction and, Complex Reactions
Important Questions on Rate Equation
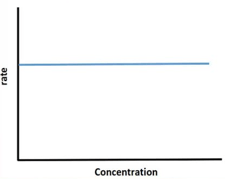
The sum of the powers of the concentration terms in the experimentally determined rate equation is known as:
A first order reaction is complete in minute. Calculate the time taken for the reaction to be complete:
,
The rate constant for the reaction, is . If the rate is , then the concentration of is
In a first-order reaction, the concentration of reactant decreases from in. The rate constant of reaction in is
Consider a reaction . When concentration of both the reactants G and H is doubled, the rate increases by eight times. However, when concentration of G is doubled keeping the concentration of H constant, the rate is doubled. The overall order of the reaction is:
Consider a reaction . When concentration of both the reactants and is doubled, the rate increases by eight times. However, when the concentration of is doubled, keeping the concentration of constant, the rate is doubled. The overall order of the reaction is:
Consider the chemical reaction:
The rate of this reaction can be expressed in terms of time derivatives of concentration of Identify the correct relationship amongst the rate expressions:
Hydrogen gas, , reacts with iodine gas, , to form hydrogen iodide, :
The mechanism of the two-step reaction is considered to be:
step : fast
step : slow
What is the rate equation for the overall reaction?
Give the name of the catalyst that used in the contact process.
Draw a graph between rate and concentration of reactants for first order reaction.
The graph between rate and concentration of reactants for second order reaction is
The plot of 1/[A] versus time is a straight line with k = slope of the line. Other graphs are curved for a second order reaction.
Explain second order reaction with an example ? Draw the graph between 1/A vs time for second order reaction.
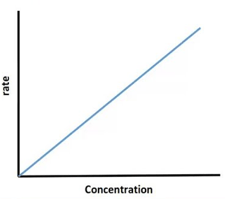
The graph between rate and concentration of reactants for first order reaction is
Draw a graph between rate and concentration of reactants for first order reaction.
For, a zero-order reaction, the plot of concentration of reactant versus rate is linear with negative slope and zero intercept.
